Collection Metadata Management
Time to complete: 20 minutes
In this guide we'll walk you through how to store media using the Sequence Collections API with Cloudflare Workers, as well as read from the Metadata API to render images
This can be accomplished with 8 steps
- Obtain a Secret API Key from the Sequence Builder Console
- Create Collection from a cURL request one time
- Create Token create a token using a tokenID
- Create Asset create an assetID
- Store an Image process and store an image
- Update to Non-private update an asset to be non-private
- Publish Collection from a cURL request one time
- Render Asset from API from a cURL request one time
First follow this section of the Collectible Minting Service Guide guide to create a cloudflare worker
1. Obtain a Secret API Key
In order to use the backend service, a Secret API Key must be obtained to authenticate requests to your project
First start by accessing settings, and selecting the API Keys from the Sequence Builder Console
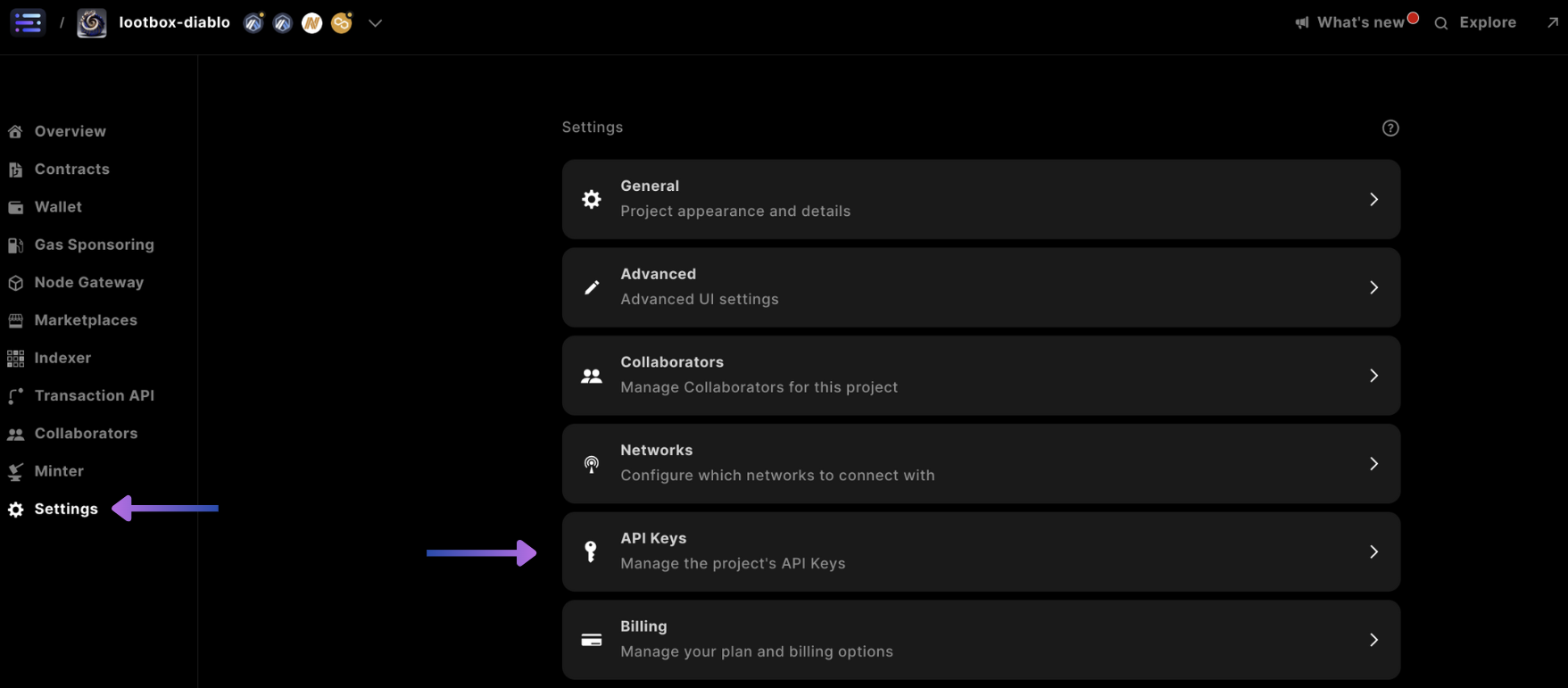
Scroll down and select + Add Service Account
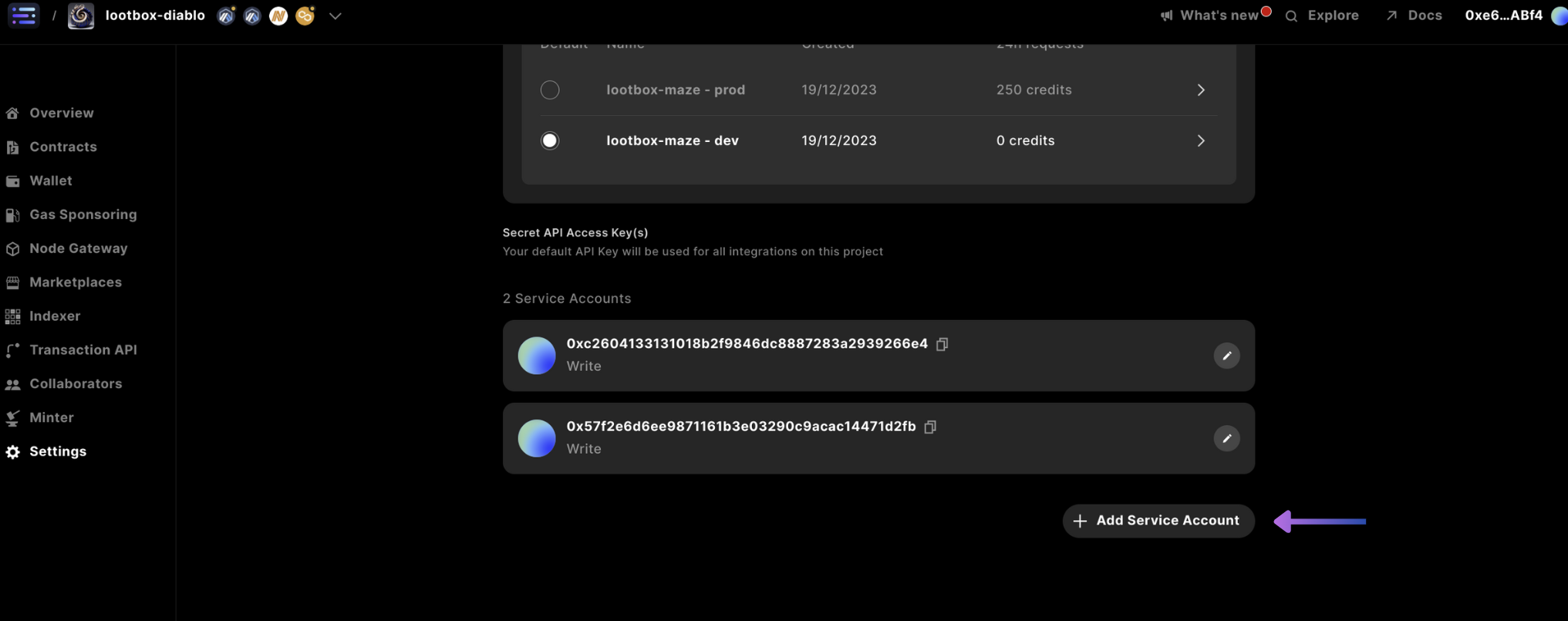
Then change the access to write and confirm
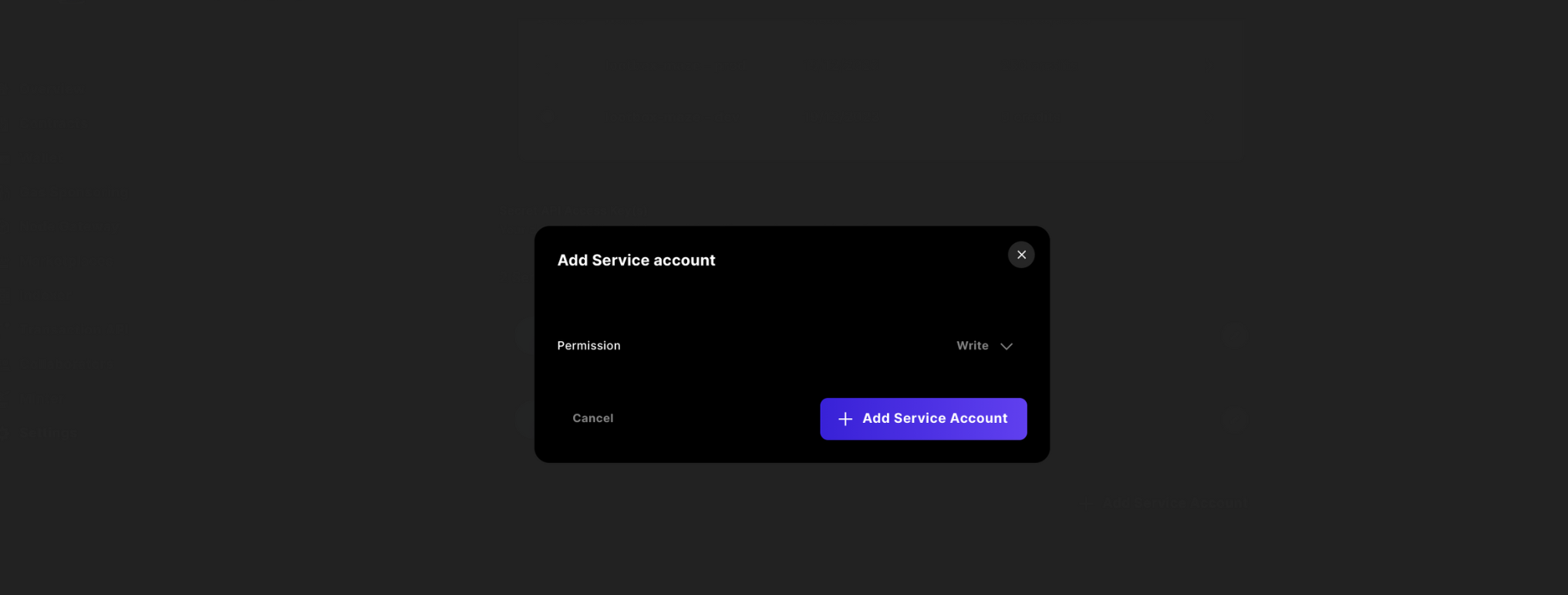
Finally copy the key and store it in your wrangler.toml as JWT_ACCESS_KEY, as you will not have access to this in the future from the Sequence Builder Console.
2. Create Collection from a cURL Request
As a one time requirement to uploading media to the service, a collection has to be first made. By using the Secret API Key and projectID retrieved from the Builder Console
We call the service to retrieve a collectionID
curl --location 'https://metadata.sequence.app/rpc/Collections/CreateCollection' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <secret_API_key or jwt_access_key>' \
--data '{
"projectId": <project_id>,
"collection": {
"metadata": {
"name": "<collection_name>",
"description": "<description>",
"external_link" : "<https://link>"
},
"image": "",
"decimals": <decimals_typically_as_0>,
"properties": null,
"attributes": null
}
}'We then set the collectionID from the returned response in the wrangler.toml as COLLECTION_ID
3. Create Token using TokenID
import { ethers } from 'ethers'
...
const METADATA_URL = 'https://metadata.sequence.app'
const myHeaders: any = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
myHeaders.append("Authorization", `Bearer ${process.env.JWT_ACCESS_KEY}`);
const randomTokenIDSpace = ethers.BigNumber.from(ethers.utils.hexlify(ethers.utils.randomBytes(20)))
// TODO: create token
const stringBody = JSON.stringify({
"projectID": projectID,
"collectionID": collectionID,
"token": {
"tokenId": String(randomTokenIDSpace),
"name": "<token_name>",
"description": "<description>",
"decimals": 0,
"attributes": [
{
"trait_type": "<trait_type>",
"value": "<value>"
}
]
}
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: myHeaders,
body: stringBody,
};
const res = await fetch(`${METADATA_URL}/rpc/Collections/CreateToken`, requestOptions)4. Create Asset using TokenID
In the request, set the metadadaField (assetType) to image, with the other neccessary fields completed to return an asset response to be used in the next step
// TODO: create asset
const stringBody2 = JSON.stringify({
"projectID": projectID,
"asset": {
"collectionId": collectionID,
"tokenId": String(randomTokenIDSpace),
"metadataField": "image"
}
});
const requestOptions2 = {
method: "POST",
headers: myHeaders,
body: stringBody2,
};
const res2 = await fetch(`${METADATA_URL}/rpc/Collections/CreateAsset`, requestOptions2)
const jsonCreateAsset: any = await res2.json()5. Store Image Asset
With the passed in asset.id from the previous jsonCreateAsset object
...
const uploadAsset = async (env: Env, projectID: any, collectionID: any, assetID: any, tokenID: any, url: any) => {
const response = await fetch(url);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`Failed to fetch file from ${url}: ${response.statusText}`);
const arrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const blob = new Blob([arrayBuffer]);
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('file', blob, `image.png`); // You might want to dynamically determine the filename
let METADATA_URL = 'https://metadata.sequence.app'
// Construct the endpoint URL
const endpointURL = `${METADATA_URL}/projects/${projectID}/collections/${collectionID}/tokens/${tokenID}/upload/${assetID}`;
try {
// Use fetch to make the request
const fetchResponse = await fetch(endpointURL, {
method: 'PUT',
body: formData,
headers: {
'X-Access-Key': env.PROJECT_ACCESS_KEY,
'Authorization': `Bearer ${env.JWT_ACCESS_KEY}`, // Put your token here
},
});
// Assuming the response is JSON
const data = await fetchResponse.json();
return data;
}catch(err){
console.log(err)
}
}
...
const uploadAssetRes = await uploadAsset(env, projectID, collectionID, jsonCreateAsset.asset.id, String(randomTokenIDSpace), imageUrl)
...Where the returned uploadAssetRes.url is the media file url living on Sequence servers
6. Update Non-private Token
Now, we make the token non-private by setting a private boolean to false
const stringBody3 = JSON.stringify({
"projectID": projectID,
"collectionID": collectionID,
"private": false,
"tokenID": String(randomTokenIDSpace)
});
const requestOptions3 = {
method: "POST",
headers: myHeaders,
body: stringBody3,
};
const res3 = await fetch(`${METADATA_URL}/rpc/Collections/UpdateToken`, requestOptions3)
const json3 = await res3.json()7. Publish Collection From A cURL Request
Finally, also as a one time request, we publish the collection based on the projectID and collectionID by running the following command
curl --location 'https://metadata.sequence.app/rpc/Collections/PublishCollection' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <secrect_API_key or jwt_access_key> \
--data '{
"projectId": <project_id>,
"collectionId": <collection_id>
}'This would make the collection and all the tokens with the private flag set as false accessible publicly, while others remain hidden until changed
8. Render Asset from API Publicly
You can test your prior work, by calling this cURL request with the updated variables, which will download the file to your local terminal.
Or, you can copy and paste into a browser and see the image
Where if you used the same code, the <file_name> will be image.png
curl --location 'https://metadata.sequence.app/projects/<project_id>/collections/<collection_id>/tokens/<token_id>/<file_name>' --output stored_file.pngAnd if you were using the collection for the baseURI of an ERC721 or ERC1155 you would write to a smart contract setBaseMetadataURI the following URI
https://metadata.sequence.app/projects/<project_id>/collections/<collection_id>/tokens/And the smart contract will automatically append the tokenID to the end
Give it a try
curl https://metadata.sequence.app/projects/1229/collections/40/tokens/457657099779485875855215293997335918990635014431Or in a browser
Render Asset from API Privately
Alternatively, you can decide to keep your assets stored private, but still render the data with a header secret api key passed in with the parameters completed, and for this guide the metadata_field is set to image
curl --location 'https://metadata.sequence.app/projects/<project_id>/collections/<collection_id>/tokens/<token_id>/asset/<metadada_field>' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <secret_api_key or jwt_access_key>' \
--output stored_file.png
